Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) News Brief: March 10-17, 2025
News Summary
Nature: Published research on fabrication of mRNA encapsulated lipid nanoparticles using SMART-MaGIC technologies.
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics: Released article on model-informed drug development applications for mRNA-LNP therapeutics.
Generation Bio: Reported application of T cell-selective lipid nanoparticle for developing siRNA therapeutics for autoimmune diseases.
ScienceDirect: Published research exploring the comparison of DOTMA versus DOTAP lipid nanoparticles for optimizing mRNA delivery through microfluidic methods.
Detailed News Summaries
Nature Research on SMART-MaGIC Technology for LNP Production
Nature published research on the fabrication of erythropoietin (EPO) mRNA encapsulated lipid nanoparticles using a patented technology called Sprayed Multi Absorbed-droplet Reposing Technology (SMART) coupled with Multi-channeled and Guided Inner-Controlling printheads (MaGIC). The study demonstrated the creation of LNPs with a narrow size distribution of approximately 200 nm when using SMART alone, which could be further reduced to approximately 50 nm with the SMART-MaGIC combination.
The researchers optimized their formulation by studying various N/P ratios, with N/P ratio of 5 showing over 50% cell viability in toxicity tests. The gel retardation assay demonstrated strong encapsulation of mRNA with lipid at N/P ratios greater than 1. The authors concluded that this fabrication method could have significant potential for point-of-service or distributed manufacturing of mRNA-loaded LNPs for various therapeutic applications.

Release Date: March 11, 2025
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics Article on mRNA-LNP Applications
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics journal published an article titled "Model-Informed Drug Development Applications and Opportunities in mRNA-LNP Therapeutics." The article appears to focus on model-informed approaches to developing drugs that utilize mRNA-LNP technology.
Release Date: March 14, 2025
Authors: Jiawei Zhou, Rohit Rao, Monica E. Shapiro, Nessy Tania, Cody Herron, Cynthia J. Musante, Jim H. Hughes
Generation Bio's T Cell-Selective LNP Technology
Generation Bio announced in its business highlights and financial results that they are applying their T cell-selective lipid nanoparticle technology to develop siRNA therapeutics specifically targeting T cell-driven autoimmune diseases. According to CEO Geoff McDonough, M.D., this technology addresses a significant challenge in siRNA therapeutics by selectively reaching T cells while sparing broader immune cells and achieving potent knockdown of genetic targets in vivo.
The company believes that combining their cell-targeted LNP platform with the genetic precision of siRNA will enable them to reach high-value targets that cause T cell-driven autoimmune diseases but have been undruggable or poorly addressed by conventional therapeutic approaches. Generation Bio plans to announce their lead target and indication by mid-year 2025 and reports a healthy cash balance of $185.2 million, which they expect will fund operations into the second half of 2027.

Release Date: March 13, 2025
Location: Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA
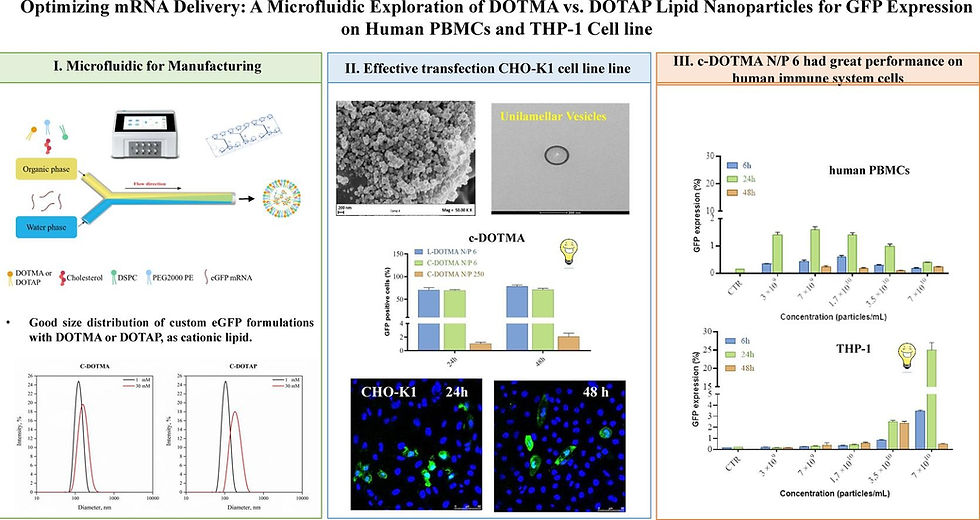
ScienceDirect Publication on DOTMA vs. DOTAP Lipid Nanoparticles
A new research paper titled "Optimizing mRNA delivery: A microfluidic exploration of DOTMA vs. DOTAP lipid nanoparticles for GFP expression on human PBMCs and THP-1 cell line" has been published on ScienceDirect. The study compares the effectiveness of two different cationic lipids - DOTMA (1,2-di-O-octadecenyl-3-trimethylammonium propane) and DOTAP (1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane) - in lipid nanoparticle formulations for mRNA delivery. The researchers utilized the Flex-M instrument and LipidFlex reagent from PreciGenome for lipid nanoparticle preparation, demonstrating the versatility of this microfluidic platform.
This research builds upon previous findings that cationic lipid-based LNPs have been widely proven to deliver antigens, DNA, and mRNA, with acceptable safety profiles. DOTAP, in particular, has been one of the most widely used cationic lipids, maintaining positive charge at all physiological pH levels and effectively concentrating anionic mRNA. The newly published paper explores the optimization of these formulations using microfluidic methods to evaluate GFP expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and THP-1 cell lines, which are important immune cell models.
The performance comparison between DOTMA and DOTAP is significant as previous research has shown that the ratio of cationic lipids to helper lipids like DOPE can be adjusted to selectively target specific cells. This aligns with earlier LinkedIn posts from Curapath in February 2025, which highlighted similar research comparing these cationic lipids in LNP formulations benchmarked against commercial formulations.
Release Date: March 15, 2025
Comments